Export and import of global automations
Applies to version: 2025 R2 and above; author: Krystyna Gawryał
Related documentation
A detailed description of the functionalities mentioned herein and their configuration can be found in the following sections of the WEBCON BPS Help:
Introduction
Global automations in WEBCON BPS are universal mechanisms that can be used repeatedly in different business processes without having to be defined each time. Version 2025 R2 introduces the ability to save such automations to a file and import them into another installation and/or environment. This article describes the key features of this functionality along with a business example of its use.
Business case
The company manages a fleet of cars and needs to monitor their technical condition, maintenance schedules and fuel consumption. A dedicated global automation has been prepared on the DEV environment to facilitate the car fleet management process, which will be integrated with other processes. The automation is to be imported to the TEST environment for testing prior to implementation in the production environment.
Global automation and its content
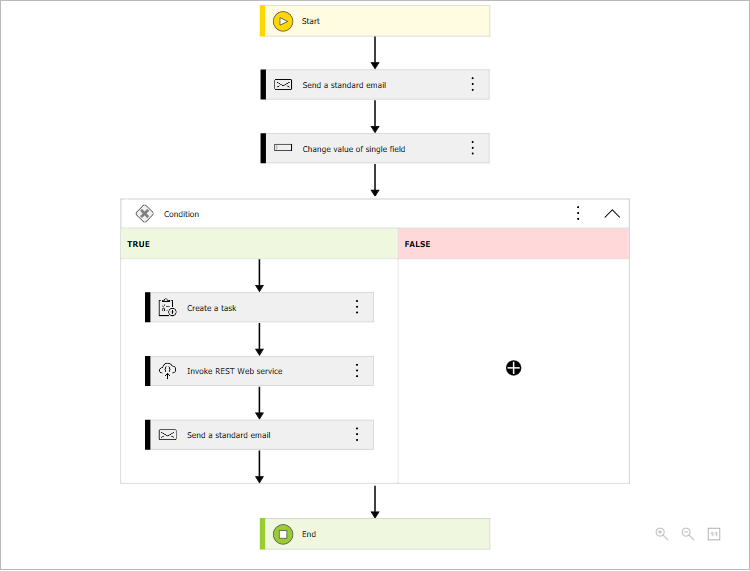
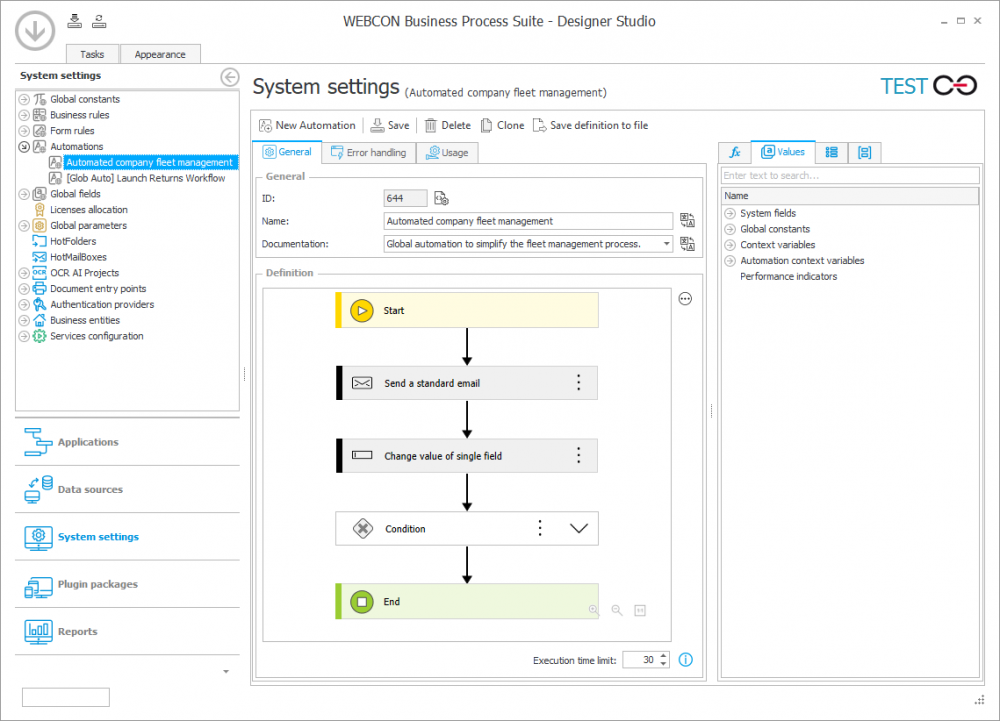
The definition of the proposed global automation is as follows:
Action 1: Send standard email
When an inspection is scheduled, the system automatically sends a notification to the vehicle user and the Administration Department.
Action 2: Change value of single field
After the inspection, the system updates the vehicle status to “Inspected" and resets the notification counter. The vehicle is ready for use.
Action 3: Create a task
If the vehicle has a reported defect, the system creates a task for the Technical Department to verify the problem.
Action 4: Invoke REST Web service
The system automatically sends a request to an external car service via API and books an inspection appointment.
Action 5: Send standard email
A notification is sent to the vehicle user and the Administration Department that the vehicle is temporarily out of service.
Saving an automation to a file
Once the global automation to be shared ("Automated company fleet management”) has been created and saved, it can be exported to a .bpa file by selecting Save definition to file from the top menu or context menu of the global automation tree. The file is saved to the specified location on the local disk.
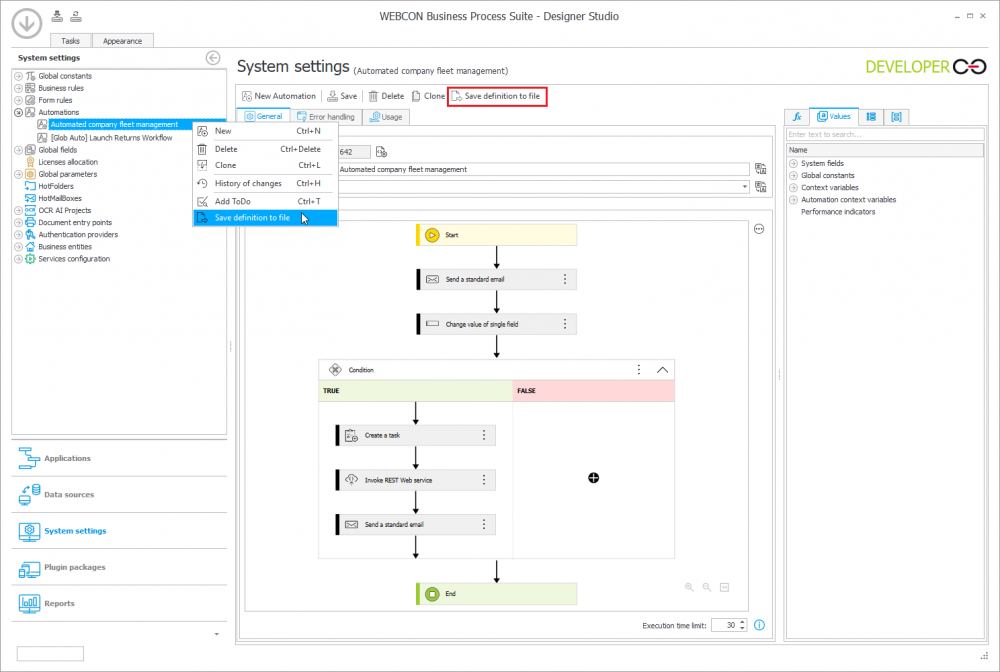
Note: Creating a file with a global automation definition will not be possible if it contains references to another Global automation, Global business rules, Global constants, Data sources, or SDK plugins. In this case, an appropriate message is displayed and the configuration of the exported automation must be modified.
If the automation definition contains references to Connections, any sensitive data present in their configuration, such as user logins and passwords, client secrets, etc., will be removed during export.
Loading an automation definition from a file
To import the "Automated company fleet management" automation into the TEST environment, select Load definition from file from the top menu or context menu of the main global automation tree.
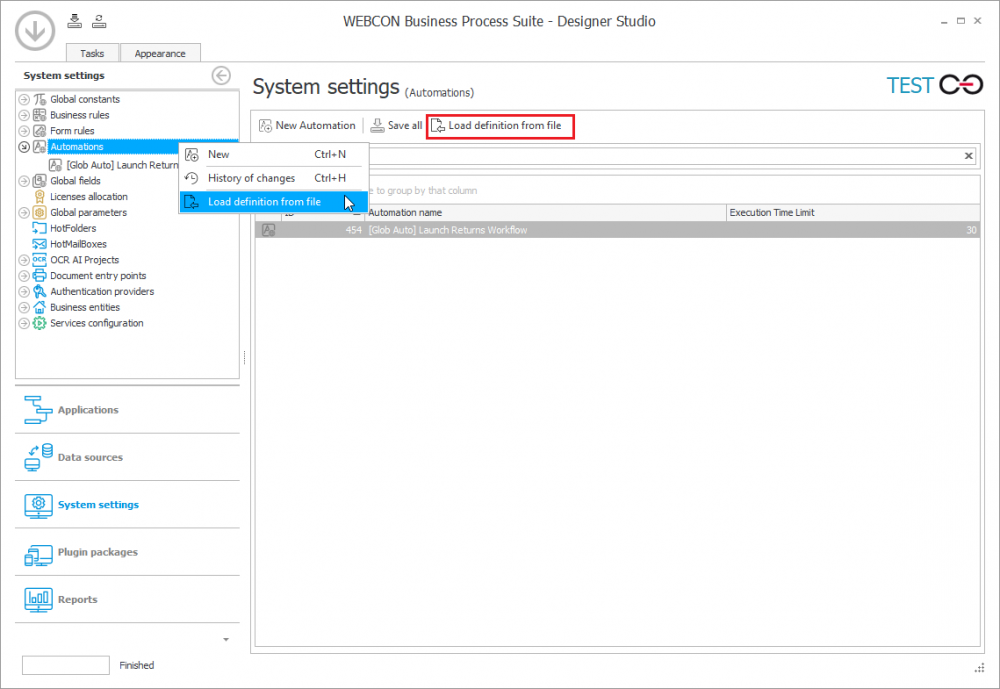
Once the location of the .bpa file is specified, the Automation configuration import wizard is launched. The import steps are described below.
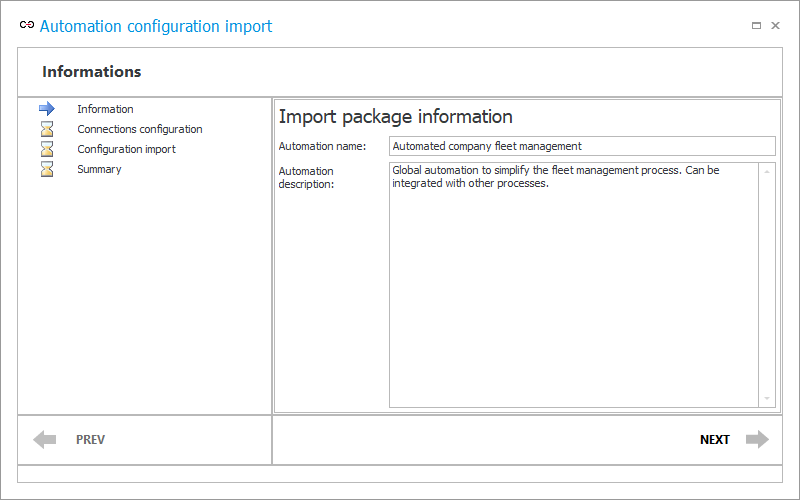
1. Information
This step displays basic information about the imported automation – its name and description. This information is editable. (To proceed to the next step of the wizard, click NEXT each time. To return to the previous step, click BACK).
2. Connection configuration
The imported global automation configuration contains an Invoke REST Web service action that required a connection to an external environment to be defined. If such a connection is not available on the target environment, it must be reconfigured so that the import of the automation configuration can continue and the action will work properly later.
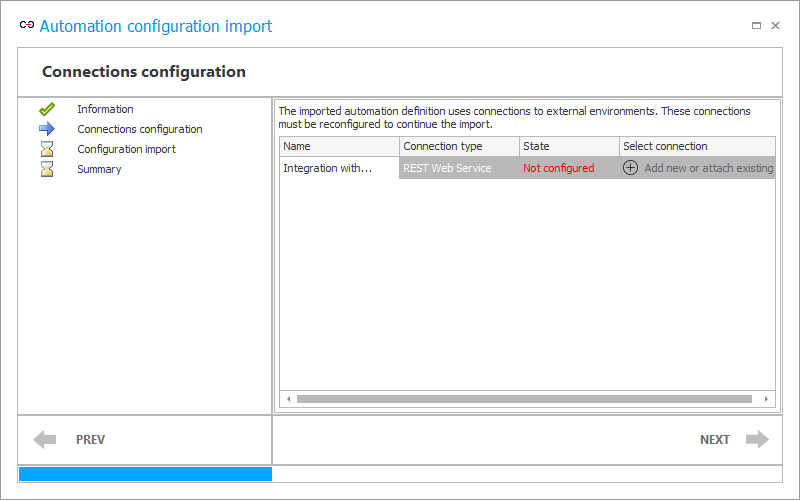
The current step displays a table with a list of all connections in use and their type. At this stage, the State column shows Not configured, highlighted in red. Here you can specify your own connection of a given type or use the one provided with the automation definition. To do so, select Add new or attach existing.
The connection selection window appears. In this case, the connection definition will be imported from the global automation being imported, so select Add new.
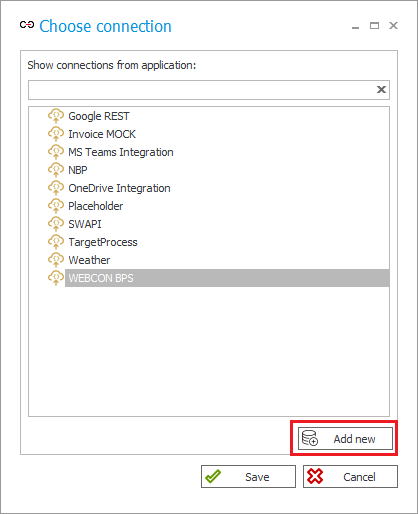
This will open the configuration window of the imported connection called “Integration with service system”.
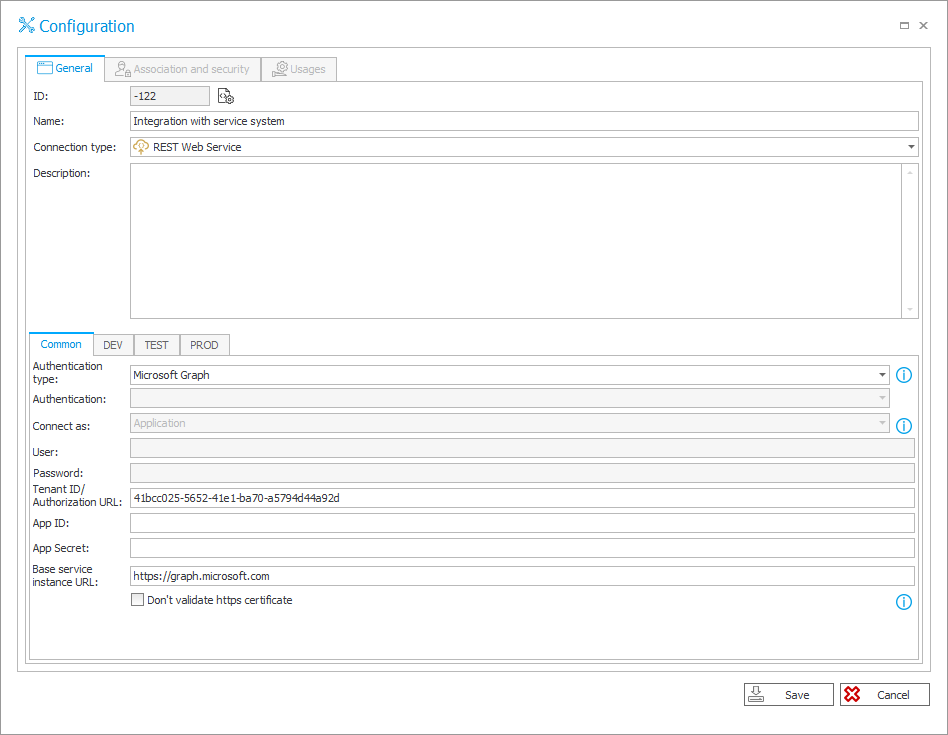
Sensitive data such as App ID and App Secret have been automatically removed from the imported connection configuration data. Completing this information is necessary for both the connection and the automation to work properly on the target environment (TEST). However, it can be skipped at this stage by clicking Save. Connection names that need to be completed after import are highlighted in red.
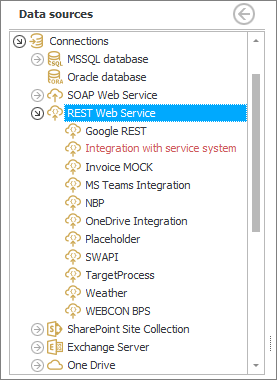
After making the above settings, the State column will display Configured in green and the Next button will become active again.
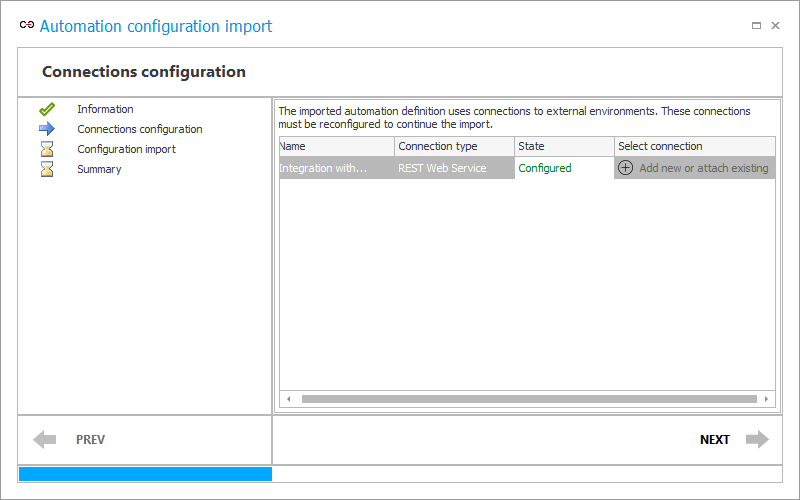
3. Configuration import
This step is the actual import of the global automation configuration. However, no user action is required here (other than clicking Next). The import may take a few seconds.
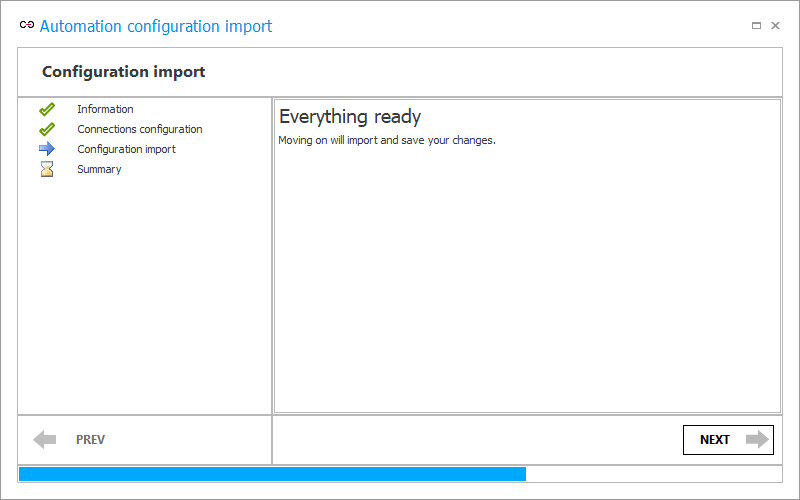
4. Summary
This step displays summary information about the import. Select Finish to exit the wizard.
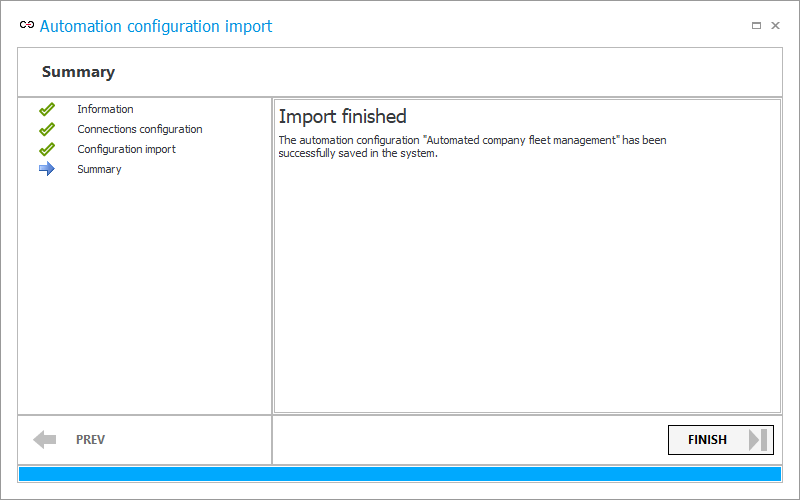
As intended, the configuration of the global automation "Automated company fleet management" was successfully stored in the target environment and can be tested before deployment in the production environment.
Summary
Global automations in WEBCON BPS allow the same mechanisms to be used multiple times in different business processes. Version 2025 R2 introduces functionality that allows global automations to be saved to a file and loaded later, thereby transferring their configuration between different environments and installations. This allows organizations to test and deploy optimized processes faster, minimizing the risk of errors and saving time.

