Path transition authorization
Applies to version: 2023 R3 and above; author: Krystyna Gawryał
Introduction
In the 2023 R3 version of BPS, WEBCON has implemented a new functionality that enhances security against unauthorized path transition .and prevents the execution of an unrequested task, such as signing a contract. If enabled, users who want to proceed to the next step must confirm their identity based on an additional authorization operation.
This article details the Path transition authorization and related system changes.
Configuration and operation principles
Path transition authorization provides additional authentication that prevents unapproved access to tasks in the process. This protects against unauthorized use, such as when an employee leaves their workstation and another employee occupies it. Access to the data will either be one-time (single path transition) or time-limited, and users will be required to perform an additional authentication operation.
To support this functionality, the Path transition authorization option has been added to the Parameters tab in the path configuration with the following settings:
-
- Require – one authorization is required for the entire authorization session. The authorization session lasts 5 minutes by default, but this value can be changed globally for the environment. During the session, the end user may go any number of times through any path (on any workflow instance) for which this authorization mode is set. When the authorization session expires, a new authorization is necessary,
- Always require – each path transition requires authorization. In this mode, the authorization session is related to a specific instance presented to the user at the time of authorization and to a specific path. Therefore, additional authorization in “Always require” mode configured on a subpath is impossible and will always fail.
A new authorization in “Always require” mode refreshes the authorization session for “Require” mode. This means that for the duration of the refreshed authorization session, the end user may go any number of times through paths that have the authorization mode configured as “Require”.
-
- None – no additional authorization is required.
If Back to the previous step is set as the target step in the path configuration, the option to authorize a path transition will remain inactive.

Fig. 1. Configuration of the Path transition authorization
The authorization methods to be used by the end user are defined by the system administrator in the Available authorization methods section under System settings → Global parameters → Security.
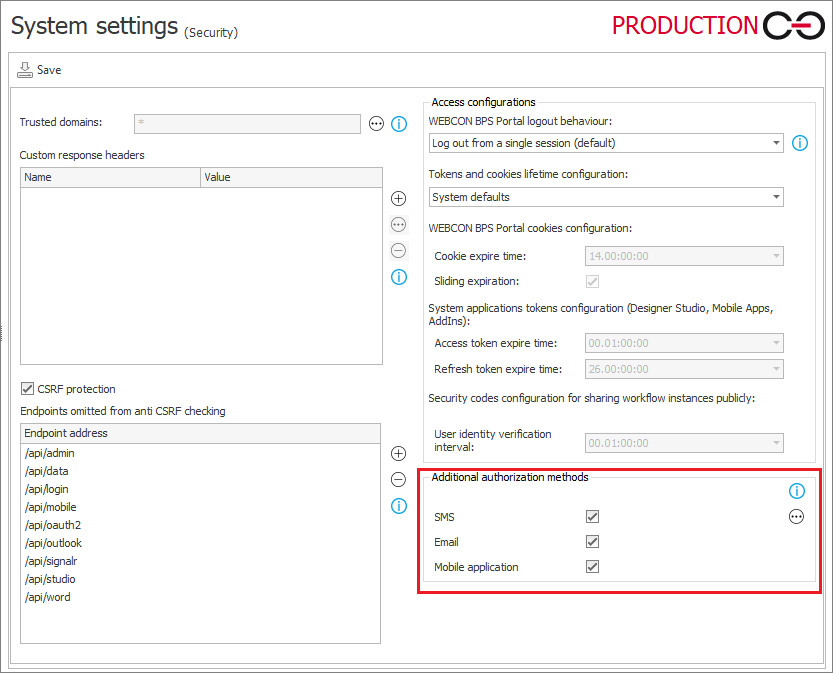
Fig. 2. Choice of authorization methods available to the user
If the path is configured with the Require or Always require mode selected, and the administrator allows any authorization method (see Fig.2), the following window will appear during the path transition attempt:

Fig. 3. Selecting the path authorization method
The appearance of the window may vary depending on the system settings mentioned above, or it may not appear at all if only one of the authorization methods is selected. It allows the user to select the authorization method: a one-time authorization code will be sent to the user's email address (email message), phone number loaded from Active Directory and defined in the user's profile (SMS), or to the mobile application (PUSH notification).
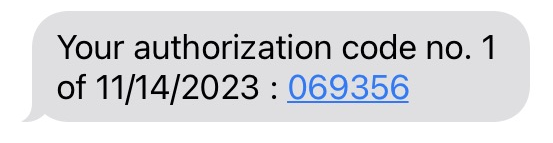
Fig. 4. SMS with authorization code
The received authorization code must be entered in the form window:
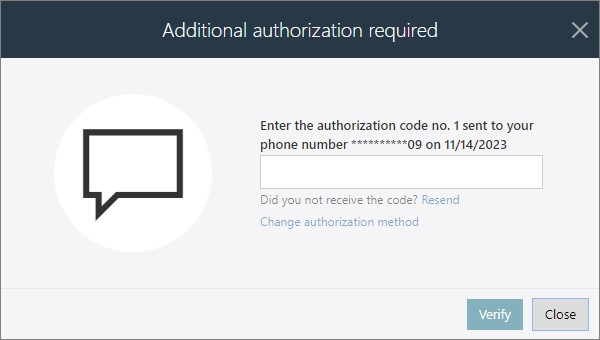
Fig. 5. Form window for entering the authorization code
Entering the code is equivalent to confirming the user's identity, and once authorized, the user may continue working with the instance(-s) once or for the duration of the session.
Note that a user can have only one authorization session active at a time – starting a new session automatically invalidates the previous one.
If the path has been configured with the Always require option selected, the path transition will require additional authorization, even if the user already has an active authorization session. The previous session is invalidated, and proceeding to the next step in the workflow requires re-entering the one-time authentication password.
It is worth noting that in case of active Substitution, when a user replaces another employee, i.e. works on their behalf or the replaced person’s tasks are delegated to the user, and the substitute goes through a path that requires additional authorization, a one-time code will automatically be sent to the substitute's email/phone number/mobile application. This means that the substitute will always authenticate the authorization session with their own data.
MailApproval, HotFolders, HotMailBoxes, WEBCON BPS Workflow Service
If going through a path requires periodic authorization or must always be authorized, it cannot be used for the MailApproval functionality, whose configuration tab is then unavailable. If you attempt to set an approval requirement for a Path with MailApproval enabled, you will receive an appropriate message.

Fig. 6. A message informing about the inability to change
the authorization settings of the path with MailApproval enabled
Similar restrictions apply to HotFolders and HotMailBoxes. Documents and attachments processed in the context of these functionalities cannot be transferred through a path for which an additional authorization is required.
If the path transition is implemented by WEBCON BPS Workflow Service (e.g. automatic start of the workflow, execution of Cyclical actions, actions executed On Timeout), the configuration of an additional authorization on that path will lead to an operation execution error.
Authorization for Quick paths and Mass actions
The functionality also works in certain cases when using Quick paths. If the user configures a Quick path with periodic or each-time authorization, the received code can be used to move single or multiple workflow instances through that path at the same time, for example, from the Report or My tasks level, without having to enter form edit mode.
A similar authorization solution is provided for users of Mass actions on reports. When configuring Mass action buttons, the user can select a path for which a periodic or each-time authorization requirement has been set. The code received is then used to authorize the simultaneous movement of multiple report elements through that path.
Path transitions in subworkflows
The functionality of path transition authorization affects how automatic subpath transitions are handled, i.e. when an instance is started in a new workflow or subworkflow, for example, by triggering an action or automation. Therefore, it is necessary to follow these configuration rules:
- It is not recommended to configure additional authorization for path transitions in subworkflows (None).
- However, if the user wants to configure a separate authorization for a subpath transition, they should select periodic authorization (Require). Validation will then take place, and the subpath transition will succeed only if periodic or each-time authorization (Always require) is configured also for the path in the parent workflow and that session is still active.
- Path transition in a subworkflow that is configured to require authorization every time (Always require) will never be successful, even if the path in the parent workflow is also configured to require authorization every time. For this reason, it is recommended to use the solution from point 2) for paths in subworkflows.
Summary
The Path transition authorization functionality provides additional protection against unauthorized access to form data and task execution. Thanks to it, the administrator, the owner of a workflow instance or the user responsible for its configuration can check who has access to and can perform operations on the workflow instances at a given step and for how long, and effectively limit this access in case of irregularities. The functionality also affects those system functions where many workflow instances are moved through the path automatically or in groups. However, it should not be considered as a restriction, but as a method of increasing the level of security of the information entered by users into the system.

