Task assignment – business rules
Applies to version: 2020.1.x and above; author: Urszula Słupik
Each WEBCON BPS workflow is a sequence of steps. On intermediate steps, there are usually tasks that must be completed by a user (or a group of users) before the instance may progress to the next step.
The tasks can be assigned in different ways:
- Based on the logic of the business application (predefined task assignment)
- By indicating the specific user or group of users
- Based on a business rule
- Dynamic, depending on the value of one of the form fields
- By using the “Create a task” action
- By using the “Add privileges” action (in some cases it is better to grant permissions to edition instead of assigning tasks)
In this article, we will focus on assigning tasks based on a business rule.
Task assignment is related to the transition path and requires setting several parameters in the Task creation tab.
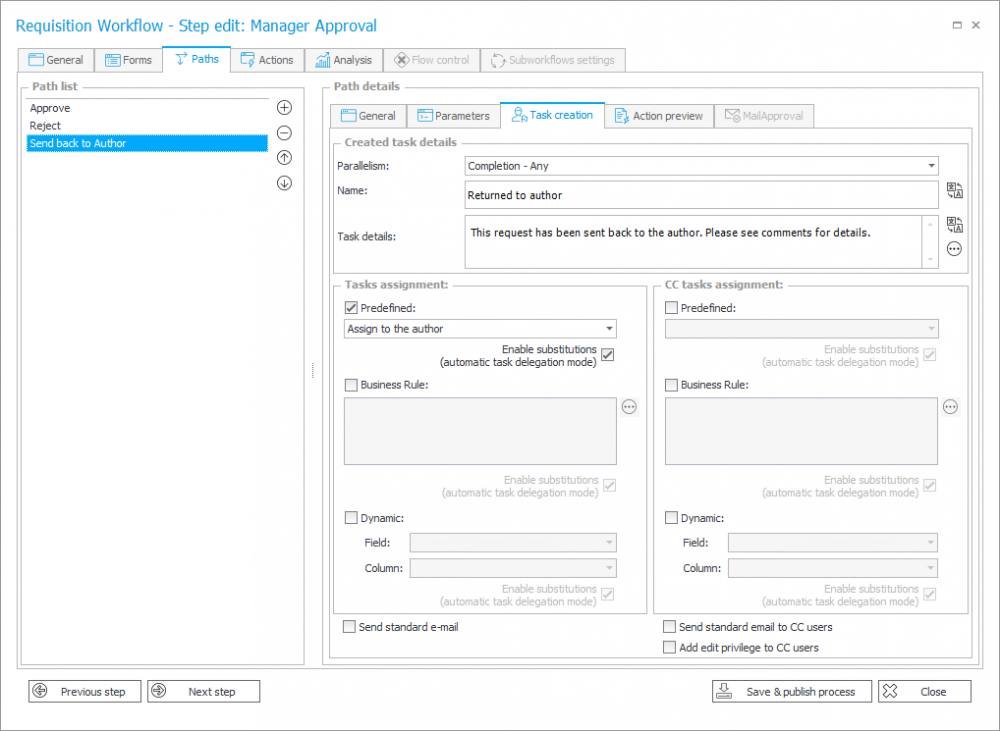
Tasks in WEBCON BPS can be assigned to several people in parallel. The “Parallelism” parameter specifies whether the task can be completed by one of them (Completion – Any) or everyone must do it (Completion – All).

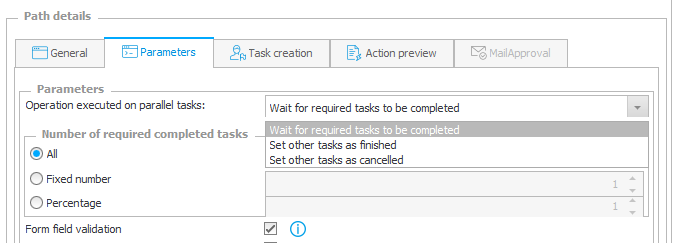
The choice of the “Completion – All” option requires defining additional parameters. You need to specify what exactly the “All” parameter will mean.
- All – all people from the indicated group
- Fixed number – a fixed number of people (e.g. two from a group of three)
- Percentage – a specified percentage of the group members
The operation executed on parallel tasks allows deciding what to happen when the first person completes the task.
For example, in the Customer Service department the task can be assigned to all employees, but if one of them first completed it – for the remaining people the task can be marked as canceled.
A detailed description of this functionality can be found at Tasks vs Privileges (webcon.com).
The predefined task assignment option allows to configure a business application based only on its logic, without indicating the specific users or groups.

For example, in the Back to the author step – the task will be forwarded to the person who started the process.
A detailed description of this functionality can be found at Predefined task assignment (webcon.com)
Based on the business rule
In the 2020 version, the “Always to” section has been replaced with the “Business rule” section.
The existing functionality (which indicates the specific users or groups from the Users list) has been expanded with the ability to create a business rule based on which the tasks will be assigned.
A. Task assignment directly to the people or groups from the Users list
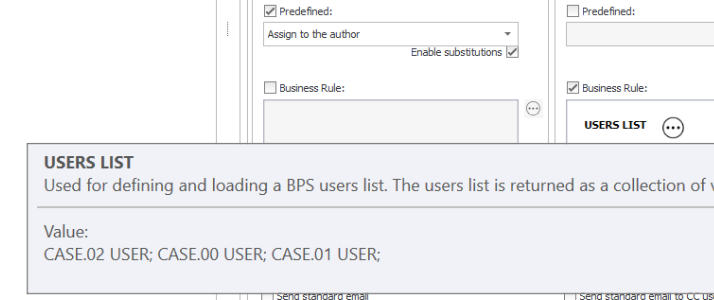
To indicate users to whom the task should be assigned, use the USER LIST function, which is available from the auxiliary list in the “Functions” tab.
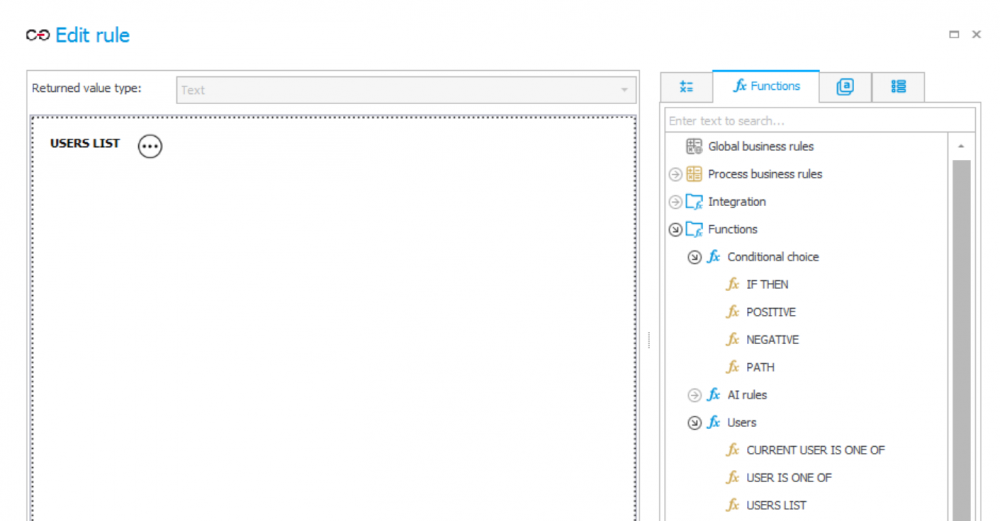
The values of the USERS LIST function are people or groups separated by semicolons. After approving the Users list, in the “Create a task” tab you can view the users in the tooltip.
B. Task assignment based on the business rule
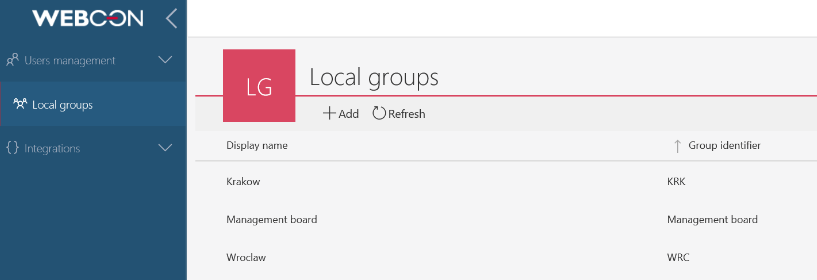
Thanks to the business rule, the tasks can be assigned by using more complex algorithms. In the example below, three BPS groups were created:
- Management board – people who manage the company and approve the orders over 1000 PLN
- KRK and WRC – the ID of groups managing departments in Kraków and Wrocław. They can make decisions about orders for their branches for smaller amounts (< 1000 PLN)
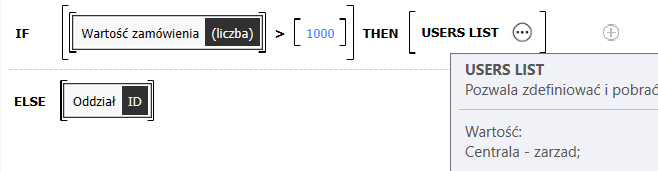
The registration of an order for goods requires information about the department which is making the order (Department form field – a choice field based on the fixed list of values) and the value of the order.
The following rule assigns the task to the Management board if the value of the order is greater than 1000 PLN. If less – the task goes to the indicated department.
C. Create a task action
The business rules can also be used during the configuration of the “Create a task” action. The “Always to” and “SQL query” sections were replaced by the “Business rules” section.
Due to the introduced changes in the functionality – during the migration process, the existing configuration of selecting users based on the SQL query and based on the “Always to” parameter will be transferred to the analogical business rule.

Dynamic task assignment
Dynamic task assignment is the ability to indicate the users or groups depending on the vale of a form field. In the example below, on the “Order registration” step its Category is indicated. In the data source list of categories, each value on the list is associated with a person responsible for the given category.
After selecting the category, the task is assigned to this person.
Task vs Privileges
There are situations where the workflow stops at some step for a longer period of time (e.g. the employee wants to receive new equipment). In this situation, the “Equipment” step will be active for a long time and with it the active tasks assigned to the employee.
The solution in this situation can be the action granting permission for the user to modify the form (without deleting) in place of tasks.
A detailed description of this functionality can be found at Tasks vs Privileges (webcon.com)